Chinese ancient architecture is the carrier of Oriental philosophy and culture, with a long history and brilliant achievements
. 
Its unique style is shining in the world architectural history
. 
These vivid and real ancient buildings are full of profound culture, telling us the true history
. 
The characteristics of ancient single building are concise, real and organic
. 
“Concise” means that the plane of traditional Chinese architecture takes “room” as the unit
. 
The plane outline and structural layout of the building are simple and clear, and the basic situation of the interior space and its superstructure can be obtained by observing the column network layout
. 
The plane “reality” of the East Hall of Foguang Temple refers to the authenticity of the structure
. 
Traditional Chinese architecture is unreservedly exposed beams, brackets, columns and other wood frame components
.
At the same time, the exposure of the structure is also beneficial to the protection of the wood frame
.
On the one hand, it can improve the ventilation conditions of the wood, and on the other hand, it is easy to find the injured and damaged situation and repair it in time
.
“Organic” in the transverse section of the East Hall of Foguang Temple means that the interior space can be divided flexibly
.
In order to meet the requirements of different functions, and easy to integrate with the environment, the indoor and outdoor space can flow into each other
.
Such as indoor and outdoor courtyard space and flowers scenery and indoor blend
.
The advantage of space treatment is completely benefited from the application of wood frame structure system
.
The art of Chinese ancient architecture has a long history
.
Different regions have different architectural styles
.
However, their traditional architecture has common characteristics in group layout, space, structure, building materials and decorative art
.
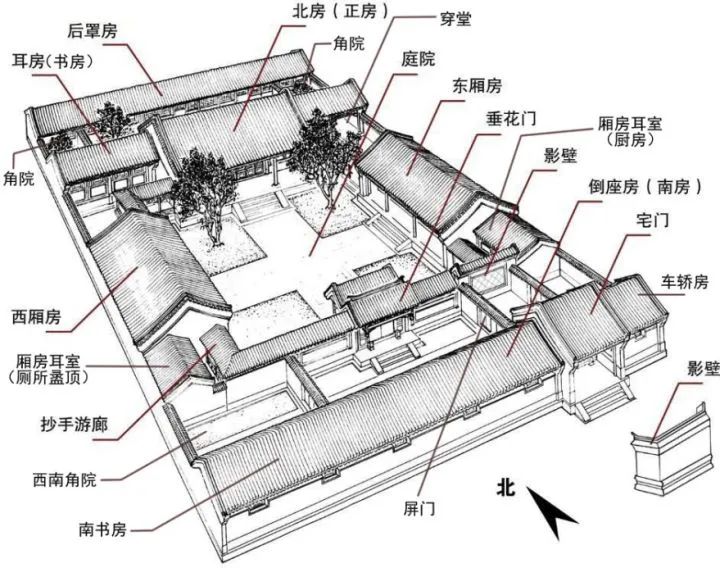
Courtyard — the plane space of the courtyard
.
The Chinese architecture courtyard is inside while the house is outside, that is, the house surrounds the courtyard
.
Houses, walls, etc
.
are enclosed into a courtyard, with the courtyard as the center; or the main unit (i.e
.
main hall, main hall) as the center, and the secondary unit (i.e
.
two chambers) around the main unit, with one main chamber and two chambers connected by a plagiarism corridor, forming a building
.
For example, the courtyard space in the local dwellings
.
Its characteristic lies in the “courtyard” as a component of the building plane, the integration of indoor and outdoor space, the corridor as a transition space, full of life
.
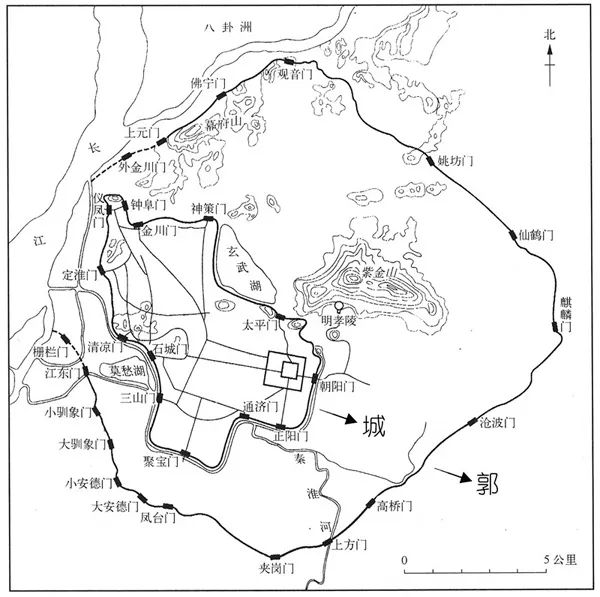
Siheyuan and Chengguo, from Siheyuan residence to the Great Wall, all belong to the same space form, that is, the inward and outward closed space form, which embodies or serves a social system
.
The state, which is widely known as the city in ancient times, means that political institutions, military strength and the vast majority of the people live in one city
.
Outside the city is the natural Guangchuan, which can live in a village and build other businesses, but it is not independent
.
The Great Wall was originally set up to defend the enemy’s territory, but in a sense, the Great Wall is just like the wall of the country
.
Whether it is the capital of all dynasties, palaces, gardens and temples, temples, ancestral temples, temples, or local dwellings and shops are characterized by this kind of courtyard space layout
.
Tuisi Garden is an introverted and hierarchical architectural space mode, especially the traditional garden
.
It is not only formal, but also artistic
.
In the garden, there are corridors, pavilions, pavilions, halls and other buildings or powder walls around the garden, and the courtyard is divided by trees, rockeries, pools, walls or buildings
.
The courtyard is so deep that it makes people feel relaxed and happy
.
The space art of axis is particular about symmetry in Chinese and foreign single buildings, but Chinese architecture and space layout are especially good at axis symmetry
.
This is mainly reflected in the architectural system which is greatly influenced by the Chinese “Zhou Li” thought
.
In the ancient capital planning, the main palace is located on the central axis, with the palace as the main body, and the secondary buildings are located on both sides, with a symmetrical layout, such as “the former dynasty and the later city”, “zuozu and YouSHE”, etc., such as the planning layout of Dadu in Tang Dynasty and Beijing in Ming and Qing Dynasty
.
For another example, in ancient Chinese temples, there are many examples of emphasizing the spatial layout of the axis
.
Generally, the main hall, the main hall and the main hall are placed on the important position of the axis, and the auxiliary hall is located around the front and back
.
“Zuoge Youzang”, “Zuozhong Yougu” and so on
.
The space is progressive and the courtyard is dense
.
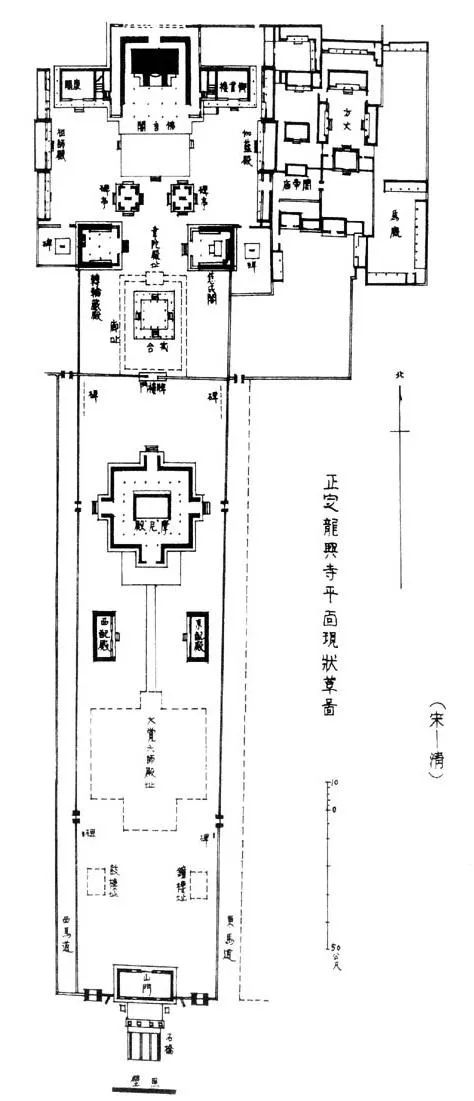
A typical example is the layout of Longxing Temple in Zhengding, Hebei Province
.
This temple was built in Sui Dynasty, rebuilt in Song Dynasty, and has been preserved up to now
.
There are subjective and objective reasons for the formation of this kind of space in traditional Chinese architecture
.
Objectively, such as natural, geographical and ecological reasons, subjectively, such as China’s long-term mode of production, economic form and human form
.
The main form of traditional wood structure is Chinese traditional architecture
.
In terms of its structure, whether it is royal palace, or various types of buildings scattered all over the world, including dwellings, its structural characteristics are unique in the history of ancient architecture in the world
.
There are two typical structural forms: 1
.
Beam lifting type, that is, the column on the roof foundation, the beam on the column, the short column on the beam, the beam on it, and the purlin on both ends of the beam; in this way, the ridge melon column is placed in the center of the top beam to support the purlin
.
This kind of structure is widely used in our country, especially in the north
.
Beam lifting type (left): the beam is supported by the column, and the beam supports the purlin through the bucket type (right): the column supports the purlin 2: through the bucket type
.
The characteristic of this structure is that the floor column with smaller column diameter and closer column spacing directly supports the purlin with short columns, and there is no beam between the columns, but several through braces are used to connect them, and the overhanging braces are used to support the eaves
.
This kind of structure uses small materials, but the interior columns are dense and the space is not open enough, so it is widely used in southern China
.
Because it is mainly wood frame, the column is load-bearing, the wall is not load-bearing, so the doors and windows can be freely arranged, reflecting the unity of form and structure
.
In the royal architecture and the important altar and temple architecture, the bucket arch is also supported between the column head and the eaves, which makes the eaves far-reaching and protects the wooden structure of the house
.
Here, on the one hand, the bucket arch is a structural component, on the other hand, it also becomes a decoration on the building, that is, taking the structural component as the decoration, the form reflects the function, the structure is real, the function is reasonable, and it is also a unity of the true, the good and the beautiful
.
But no matter what kind of building, the base, column, beam, purlin, rafter, diagonal brace and other parts of the structure are mostly exposed, and the shape is also processed into decorative components
.
The structure and components are combined with mortise and tenon, without nails
.
Roof forms are commonly used in ancient Chinese architecture
.
Traditional Chinese architecture is divided into three parts: abutment, body and roof, but the roof of traditional Chinese architecture is especially large, sometimes almost the same height as the body, and each part has a certain proportion and standard practice
.
Therefore, the fifth facade, the most special form feature of ancient Chinese architecture, is formed
.
Architecture and environment: the concept of “harmony between man and nature” advocates nature and loves nature since ancient times
.
The ancestors have long noticed the harmony and unity of “favorable weather, favorable location and harmonious people”
.
Qian Gua of the book of changes: “a man of great virtue shares virtue with heaven and earth, brightness with the sun and the moon, order with the four seasons, and good or bad luck with ghosts and gods
.
In the first place, the heaven is not perfect, and in the second place, the heaven is perfect
.
Confucianism advocates “the unity of man and nature”, while Taoism advocates “natural inaction”
.
Heaven, nature
.
Whether it is the Confucianist’s “up and down flow with heaven and earth” (Mencius · wholeheartedly), or the Taoist’s “heaven and earth coexist with me, and all things are one with me” (Zhuangzi · Qi Wu Lun), they all closely link man and all things in heaven and earth as an inseparable community, thus forming a subjective force to urge people to explore nature, get close to nature, and develop nature; On the other hand, the mountains and rivers are magnificent, and the beautiful scenery all over China inspires people’s boundless passion to love and praise nature.
.